Read Xdmf: Difference between revisions
(New page: == Reading XDMF Data == Image:TwoHex.jpg The following Xdmf XML file is a simple example of a Uniform Grid that contains two Hexahedron that share a face. There are values centered a...) |
Crayzeewulf (talk | contribs) (→Reading XDMF Data: Placed code in source tags so it get syntax highlighting. Cleaned up indentation of the code.) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
all stored directly in the XML file. | all stored directly in the XML file. | ||
<source lang="xml" line="1"> | |||
<?xml version="1.0" ?> | |||
<!DOCTYPE Xdmf SYSTEM "Xdmf.dtd" []> | |||
<Xdmf> | |||
<Domain> | <Domain> | ||
<Grid Name="TestGrid"> | <Grid Name="TestGrid"> | ||
<Topology Type="Hexahedron" NumberOfElements="2" > | <Topology Type="Hexahedron" NumberOfElements="2" > | ||
<DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" | <DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" | ||
Dimensions="2 8"> | |||
0 1 7 6 3 4 10 9 | 0 1 7 6 3 4 10 9 | ||
1 2 8 7 4 5 11 10 | 1 2 8 7 4 5 11 10 | ||
| Line 22: | Line 21: | ||
</Topology> | </Topology> | ||
<Geometry Type="XYZ"> | <Geometry Type="XYZ"> | ||
<DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" Precision="8" | |||
Dimensions="4 3 3"> | |||
0.0 0.0 1.0 | |||
1.0 0.0 1.0 | |||
3.0 0.0 2.0 | |||
0.0 1.0 1.0 | |||
1.0 1.0 1.0 | |||
3.0 2.0 2.0 | |||
0.0 0.0 -1.0 | |||
1.0 0.0 -1.0 | |||
3.0 0.0 -2.0 | |||
0.0 1.0 -1.0 | |||
1.0 1.0 -1.0 | |||
3.0 2.0 -2.0 | |||
</DataItem> | |||
</Geometry> | </Geometry> | ||
<Attribute Name="NodeValues" Center="Node"> | <Attribute Name="NodeValues" Center="Node"> | ||
<DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" Precision="8" | <DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" Precision="8" | ||
Dimensions="4 3" > | |||
100 200 300 | |||
300 400 500 | |||
300 400 500 | |||
500 600 700 | |||
</DataItem> | </DataItem> | ||
</Attribute> | </Attribute> | ||
<Attribute Name="CellValues" Center="Cell"> | <Attribute Name="CellValues" Center="Cell"> | ||
<DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" Precision="8" | <DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" Precision="8" | ||
Dimensions="2" > | |||
100 200 | |||
</DataItem> | </DataItem> | ||
</Attribute> | </Attribute> | ||
</Grid> | </Grid> | ||
</Domain> | </Domain> | ||
</Xdmf> | |||
</source> | |||
The XML is stored in the file "MyGrid.xmf". The following Python program demonstrated parsing the XML and | The XML is stored in the file "MyGrid.xmf". The following Python program demonstrated parsing the XML and | ||
retrieving the data values. | retrieving the data values. | ||
<source lang="python" line="1"> | |||
#! /usr/bin/env python | |||
from Xdmf import * | |||
reader = XdmfReader.New() | |||
dom = XdmfReader.read('MyGrid.xmf') | |||
# We now have a tree. Find the one and only Grid element | |||
grid = dom.getUnstruturedGrid(0) | |||
top = grid.GetTopology() | |||
print 'Values = ', top.getValuesString() | |||
# Release values from data when done | |||
top.release() | |||
geo = grid.GetGeometry() | |||
print 'Geo Type = ', geo.getType().getName(), ' # Points = ', geo.getNumberPoints() | |||
print 'Points = ', geo.getValuesString() | |||
geo.release() | |||
# for each Attribute, print Light Data and Values | |||
for i in range(grid.getNumberAttributes()): | |||
attr = grid.getAttribute(i) | |||
print 'Attribute ', i, ' Name = ', attr.getName() | |||
attr = grid. | |||
print 'Attribute ', i, ' Name = ', attr. | |||
# Attribute HeavyData is not Updated by default | # Attribute HeavyData is not Updated by default | ||
# there could potentially be many causing huge IO | # there could potentially be many causing huge IO | ||
attr. | attr.read() | ||
print 'Values ', attr.getValuesString() | |||
attr.release() | |||
</source> | |||
Latest revision as of 13:59, 20 May 2016
Reading XDMF Data
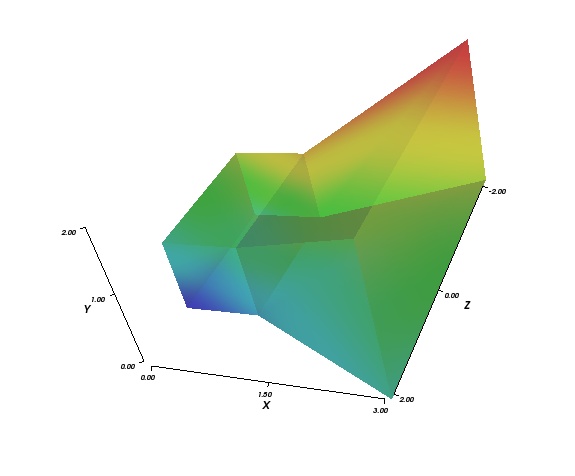
The following Xdmf XML file is a simple example of a Uniform Grid that contains two Hexahedron that share a face. There are values centered at the nodes and at the cell centers. The values for geometry, connectivity, and scalars are all stored directly in the XML file.
<source lang="xml" line="1"> <?xml version="1.0" ?> <!DOCTYPE Xdmf SYSTEM "Xdmf.dtd" []> <Xdmf>
<Domain>
<Grid Name="TestGrid">
<Topology Type="Hexahedron" NumberOfElements="2" >
<DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float"
Dimensions="2 8">
0 1 7 6 3 4 10 9
1 2 8 7 4 5 11 10
</DataItem>
</Topology>
<Geometry Type="XYZ">
<DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" Precision="8"
Dimensions="4 3 3">
0.0 0.0 1.0
1.0 0.0 1.0
3.0 0.0 2.0
0.0 1.0 1.0
1.0 1.0 1.0
3.0 2.0 2.0
0.0 0.0 -1.0
1.0 0.0 -1.0
3.0 0.0 -2.0
0.0 1.0 -1.0
1.0 1.0 -1.0
3.0 2.0 -2.0
</DataItem>
</Geometry>
<Attribute Name="NodeValues" Center="Node">
<DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" Precision="8"
Dimensions="4 3" >
100 200 300
300 400 500
300 400 500
500 600 700
</DataItem>
</Attribute>
<Attribute Name="CellValues" Center="Cell">
<DataItem Format="XML" DataType="Float" Precision="8"
Dimensions="2" >
100 200
</DataItem>
</Attribute>
</Grid>
</Domain>
</Xdmf> </source>
The XML is stored in the file "MyGrid.xmf". The following Python program demonstrated parsing the XML and retrieving the data values.
<source lang="python" line="1">
- ! /usr/bin/env python
from Xdmf import * reader = XdmfReader.New() dom = XdmfReader.read('MyGrid.xmf')
- We now have a tree. Find the one and only Grid element
grid = dom.getUnstruturedGrid(0)
top = grid.GetTopology() print 'Values = ', top.getValuesString()
- Release values from data when done
top.release()
geo = grid.GetGeometry() print 'Geo Type = ', geo.getType().getName(), ' # Points = ', geo.getNumberPoints() print 'Points = ', geo.getValuesString() geo.release()
- for each Attribute, print Light Data and Values
for i in range(grid.getNumberAttributes()):
attr = grid.getAttribute(i) print 'Attribute ', i, ' Name = ', attr.getName() # Attribute HeavyData is not Updated by default # there could potentially be many causing huge IO attr.read() print 'Values ', attr.getValuesString() attr.release()
</source>